In today’s market, the production of industrial plywood has been expanding rapidly to meet the growing demand. Plywood is not only the perfect substitute for natural wood, but it also helps address the scarcity of natural wood resources and reduces negative environmental impacts.
To produce high-quality plywood, the production process must be executed meticulously and adhere to strict technical standards. Typically, this process is divided into three main stages:
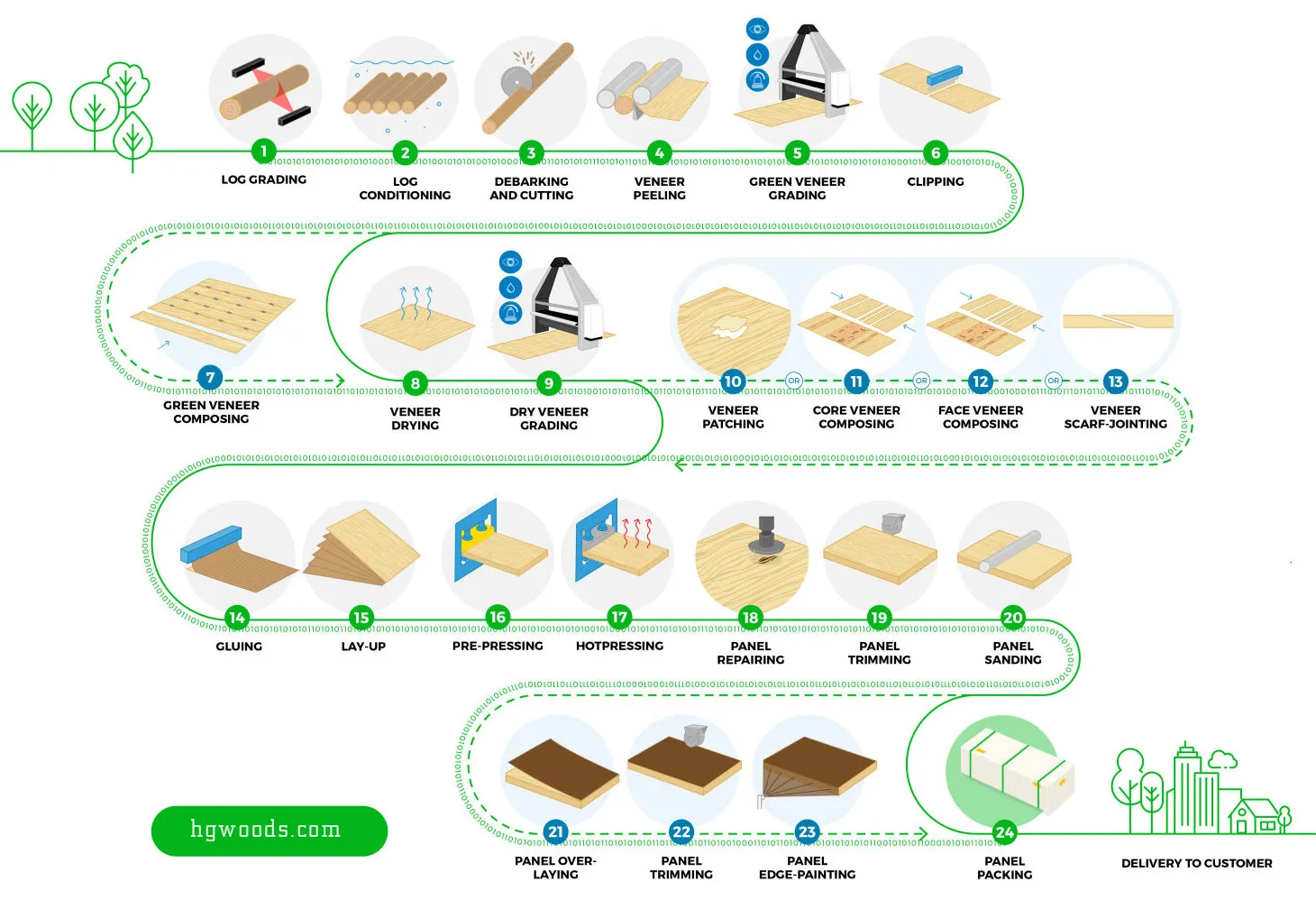
1. Stage 1: Timber Harvesting
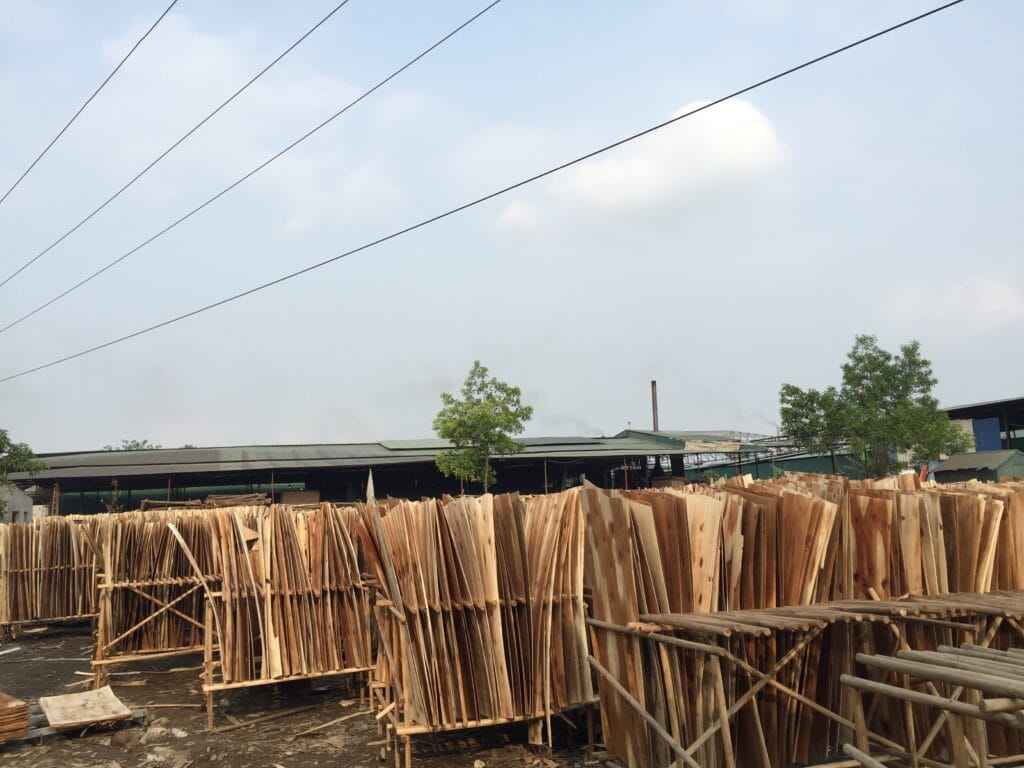
- Selecting appropriate timber: Types of wood commonly used include broadleaf trees (eucalyptus, acacia) and coniferous trees (pine).
- Initial processing: The harvested trees are stripped of branches and leaves, leaving only the main trunk.
- Transportation: The processed logs are transported to the manufacturing facility for further treatment.
2. Stage 2: Timber Processing
- Soaking the logs: The logs are soaked in water at a suitable temperature for a specified period. This step:
- Softens the wood fibers, making it easier to peel.
- Prevents cracking or warping during further processing.
- Peeling and cutting: After soaking, the logs are stripped of their bark and cut into segments of appropriate size.
3. Stage 3: Industrial Plywood Production
The production of plywood involves multiple detailed steps that require precision and adherence to strict standards:
Step 1: Bark Removal and Veneer Production
- Logs are fed into peeling machines to produce thin, uniform wood sheets (veneer).

Step 2: Drying
- The veneers are either kiln-dried or air-dried to achieve a moisture content of 6-8%.

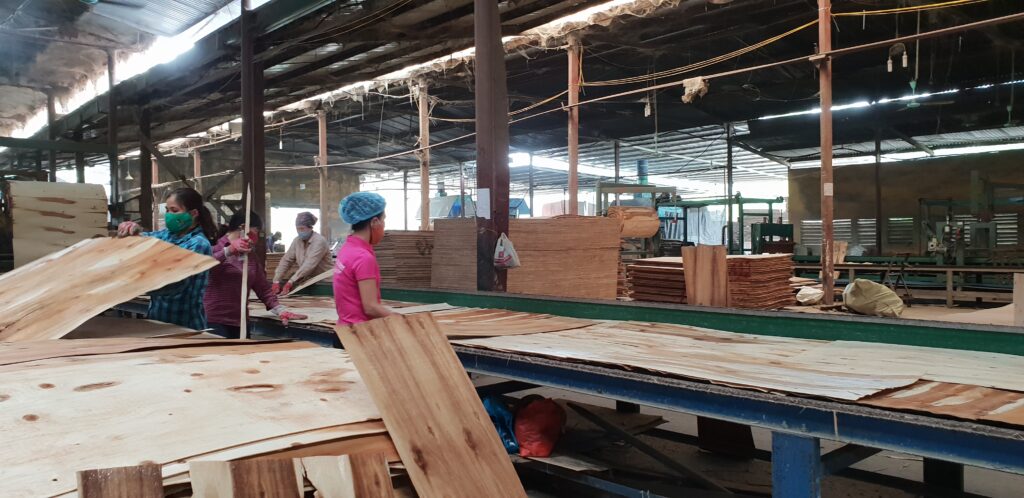
Step 3: Sorting and Quality Control
- Veneers are sorted and inspected carefully to ensure they meet quality standards before proceeding to the next stage.
Step 4: Glue Application
- Adhesives are evenly applied to the veneer surfaces. Common types of glue used include:
- Urea-formaldehyde (UF): Affordable and suitable for interior use.
- Phenol-formaldehyde (PF): Durable and water-resistant, ideal for construction applications.
Step 5: Veneer Stacking
- Veneers are stacked perpendicular to each other at 90-degree angles to enhance structural strength and prevent warping.

Step 6: Cold Pressing
- The stacked veneers are cold-pressed to distribute the glue evenly and stabilize the layers.
Step 7: Hot Pressing
- After cold pressing, the veneers undergo hot pressing under controlled pressure and temperature for a specified duration. This critical step ensures a strong bond between layers.

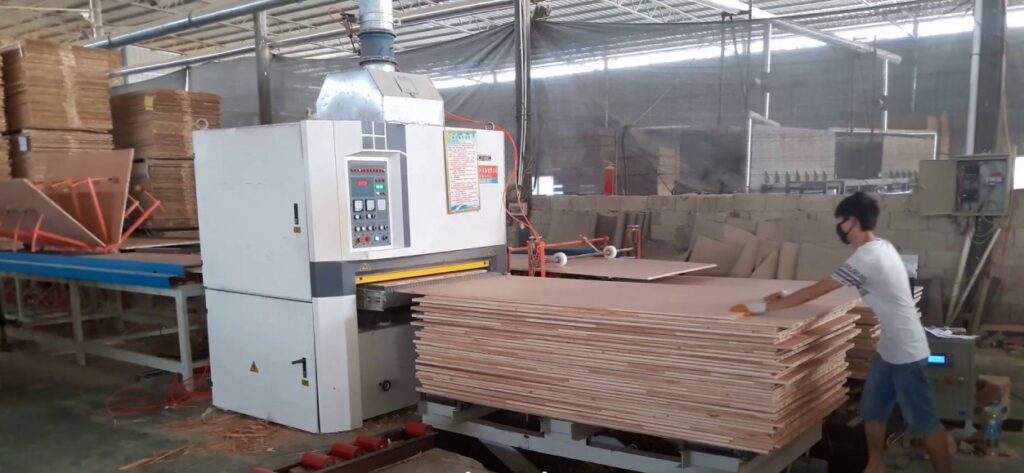
Step 8: Trimming and Sanding
- The hot-pressed plywood is cooled, trimmed to size, and sanded to achieve a smooth surface.

Step 9: Final Quality Inspection and Packaging
- The finished plywood is rigorously inspected to meet export standards. It is then strapped, palletized, and prepared for shipment.
Key Considerations in Plywood Production
- Veneer storage: Dried veneers should be stored for at least 24 hours to stabilize their moisture content before production.
- Adhesive selection: Using high-quality adhesives ensures enhanced durability and water resistance.
- Precision in pressing: Proper control of pressure, temperature, and pressing time is essential for achieving consistent product quality.
Why Choose HG Plywood?
At HG Plywood, our production process combines modern technology and years of expertise to deliver plywood products of the highest quality. Whether for domestic use or international markets, our plywood meets the strictest standards for durability, functionality, and sustainability.
Contact HG Plywood
Reach out to HG Plywood for consultations on high-quality plywood products!
H&G IMPORT-EXPORT CO., LTD
🌏 Website: hgywoods.com
☎ Hotline: (+84) 9656 09 153 (WhatsApp, Viber)
📧 Email: hgplywood@gmail.com
🏭 Address: Dinh Xuyen, Gia Lam, Hanoi

Leave a Reply